Case Report ID: 17
Title
Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca
Category
Ocular Surface Disease (3)
Description
This case presents amniotic membrane therapy to treat the corneal and conjunctival sequelae of severe keratoconjunctivitis sicca.
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca is diagnosed based on patient history, dry eye symptoms, and definite clinical signs of keratoconjunctivits sicca.
- Conjunctival epitheliopathy
- Corneal epitheliopathy
- Conjunctival hyperemia
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca is characterized by the following clinical features:
- The loss of water from the tear film increases its osmolarity above the normal limit of 311 mOsm/L
- The increase in tear film osmolarity is the link between changes in the lacrimal glands, changes in the eyelids, and disease of the ocular surface
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca evolves through a sequence of four milestones:
1. Loss of water from the tear film with an increase in tear film osmolarity
2. Decreased conjunctival goblet cell density and decreased corneal glycogen
3. Increased corneal epithelial desquamation
4. Destabilization of the cornea-tear interface
Case Report
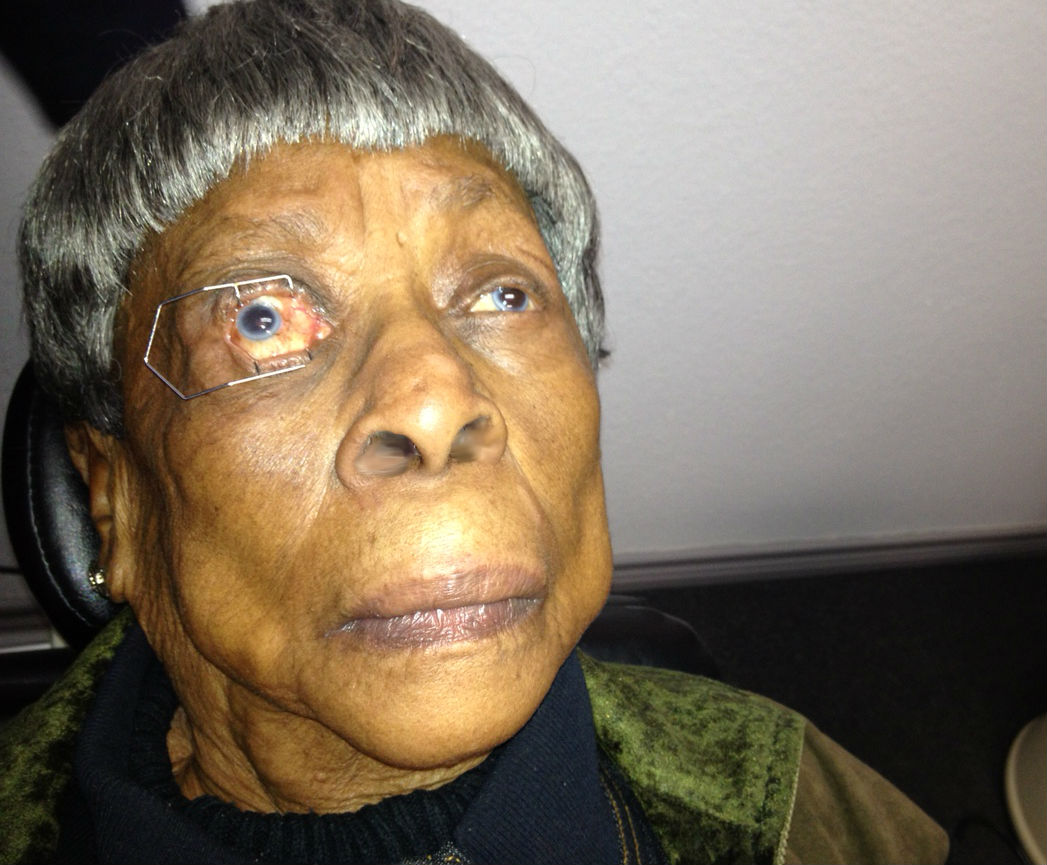
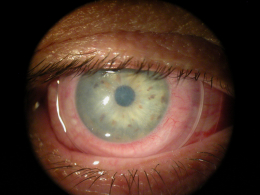
- 82-year-old White female presented with a chief complaint of severe discomfort with dry eyes and blurred vision
- Case history described cataract surgery on both eyes five months prior
- Has had dry eyes for nearly 20 years
Conclusion
xxxxx
History of Present Illness
- Associated signs and symptoms: severe discomfort
- Location: vision is worse in the right eye
- Duration: several years
- Quality: n/a
- Context: decreased vision is interfering with daily activities
- Severity: no increase in visual acuity after cataract surgery
- Timing: vision seems to be getting worse over time
- Modifiers: none
Review of Systems
The patient reported that she was in poor health and taking medications for hypertension, thyroid disease, high cholesterol, and acid reflux.
Past, Family and Social History
Non-contributory.
Uncorrected Distance Visual Acuity
- 20/200 in the right eye
- 20/60 in the left eye
Normal Examination Findings
- Mental status
- General medical observation
- Pupils
- Gross visual fields
- Basic sensorimotor examination
- External examination
- Adnexal examination
- External ocular examination with biomicroscopy
Intraocular Pressure Measurements
- 15 mm Hg in the right eye
- 16 mm Hg in the left eye
External Ocular Examination With Biomicroscopy
- Normal fundus appearance in the right eye
- Focal geographic atrophy in the left macula
Clinical Diagnosis
The clinical diagnosis is a determination based on the knowledge obtained from the patient’s medical history and from the results of the eye examination alone, without the benefit of diagnostic tests or procedures.
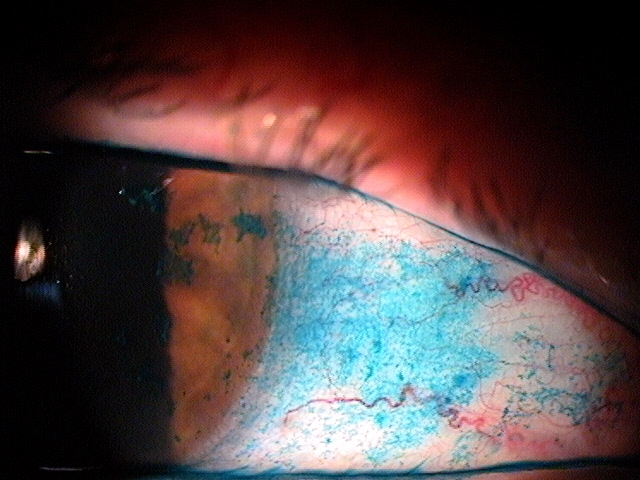
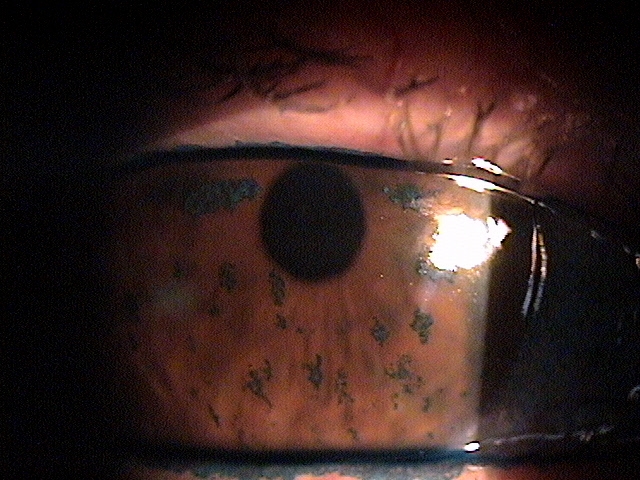
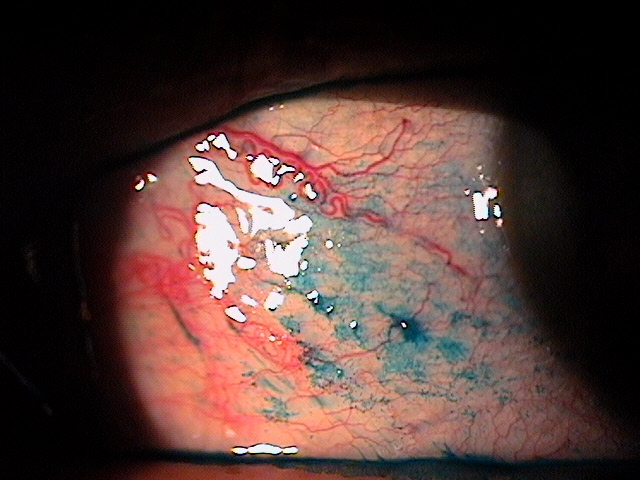
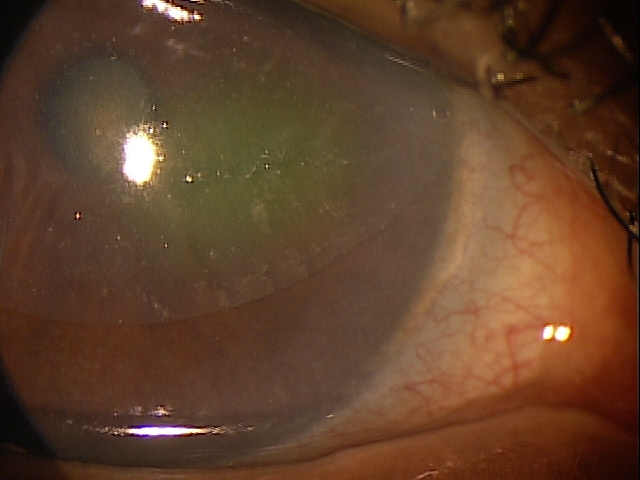
The patient’s clinical diagnosis is keratoconjunctivitis sicca based on the following clinical findings:
- Severe symptoms
- Severe conjunctival staining
- Severe corneal staining
- Corneal erosions
Treatment Plan
To gather the information required to treat keratoconjunctivitis sicca, a diagnostic and treatment program is initiated.
- Determination of different types of diagnoses
- Selection of one or more treatment options
Ordering Diagnostic Tests
When additional clinical information is needed to complete the differential diagnostic process or to assist in the treatment program, diagnostic tests or services are ordered. The performance of these tests and/or services leads to the completion of the differential diagnostic process while simultaneously initiating the treatment program.
Based on the clinical diagnosis of keratoconjunctivitis sicca, the following diagnostic tests were ordered at the conclusion of the eye examination:
- External ocular photography
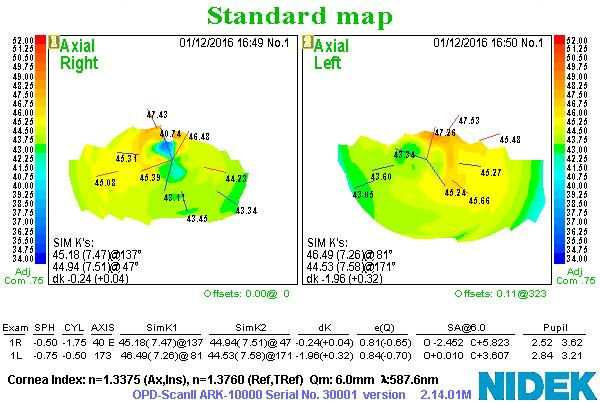
- Corneal topography
External Ocular Photography
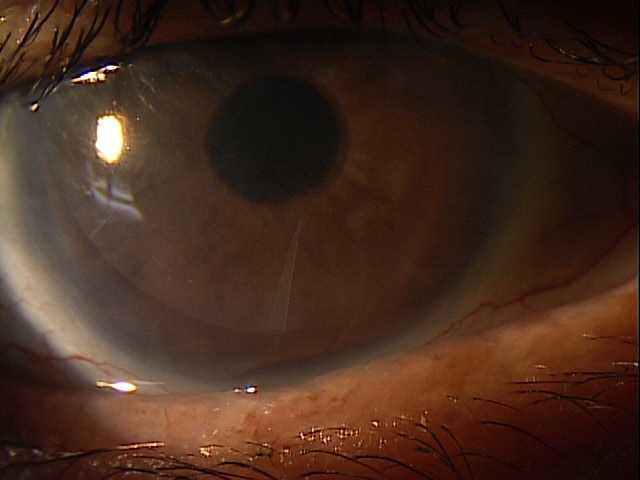
Any case of compromised tissue that could pose a threat to function could justify the medical necessity of photodocumentation. In this case, the compromised cornea tissue posed risks of infection, scarring and neovascularization. Photodocumentation of the tissue provides a baseline to monitor disease regression and efficacy of treatment.
Corneal Topography
Physical Diagnosis
Completion of the differential diagnosis process either returns you to the original clinical diagnosis or it produces a more substantiated physical diagnosis. This component of the diagnostic and treatment program, the determination of a physical diagnosis, is accomplished by studying the physical manifestations of health and illness revealed in the eye examination, the patient’s complete medical history, and supported by various diagnostic tests and procedures.
The diagnostic tests results help substantiate the physical diagnosis of keratoconjunctivitis sicca and provide a framework for monitoring changes in the disease and response to therapeutic intervention.
According to Current Procedural Terminology, when eye doctors perform ophthalmological examinations, the complexity of medical decision-making is not separated from the examining techniques used. However, as a tool to assist eye doctors in enhancing their medical decision-making skills, consider that the complexity of medical decision-making in this case report involves three components.
Diagnosis Guidelines
The first component concerns the number of possible diagnoses and treatment options that must be considered. The diagnosis and treatment of a dry eye syndrome is predicated on making the proper diagnosis and on understanding the natural history of the effects of chronic dessication on the corneal tissue.
The second component concerns the amount and complexity of medical records and diagnostic tests that have to be obtained, reviewed and analyzed. In addition to an eye examination, this visit required the review and analysis of external photodocumentation.
Third, the complexity of medical decision-making is affected by the risk of significant complications and/or morbidity associated with neurotrophic keratopathy and the risks involved in any treatment options.
Treatment Options
To begin the treatment of keratoconjunctivitis sicca, the eye doctor must firmly establish the underlying etiology. In most cases, primary treatment of the resultant corneal condition is either supportive (moisturize) or prophylactic (antibiosis). But in most cases, unless the underlying causative factor is addressed, the condition tends to become chronic and more severe.
Surgical Treatment
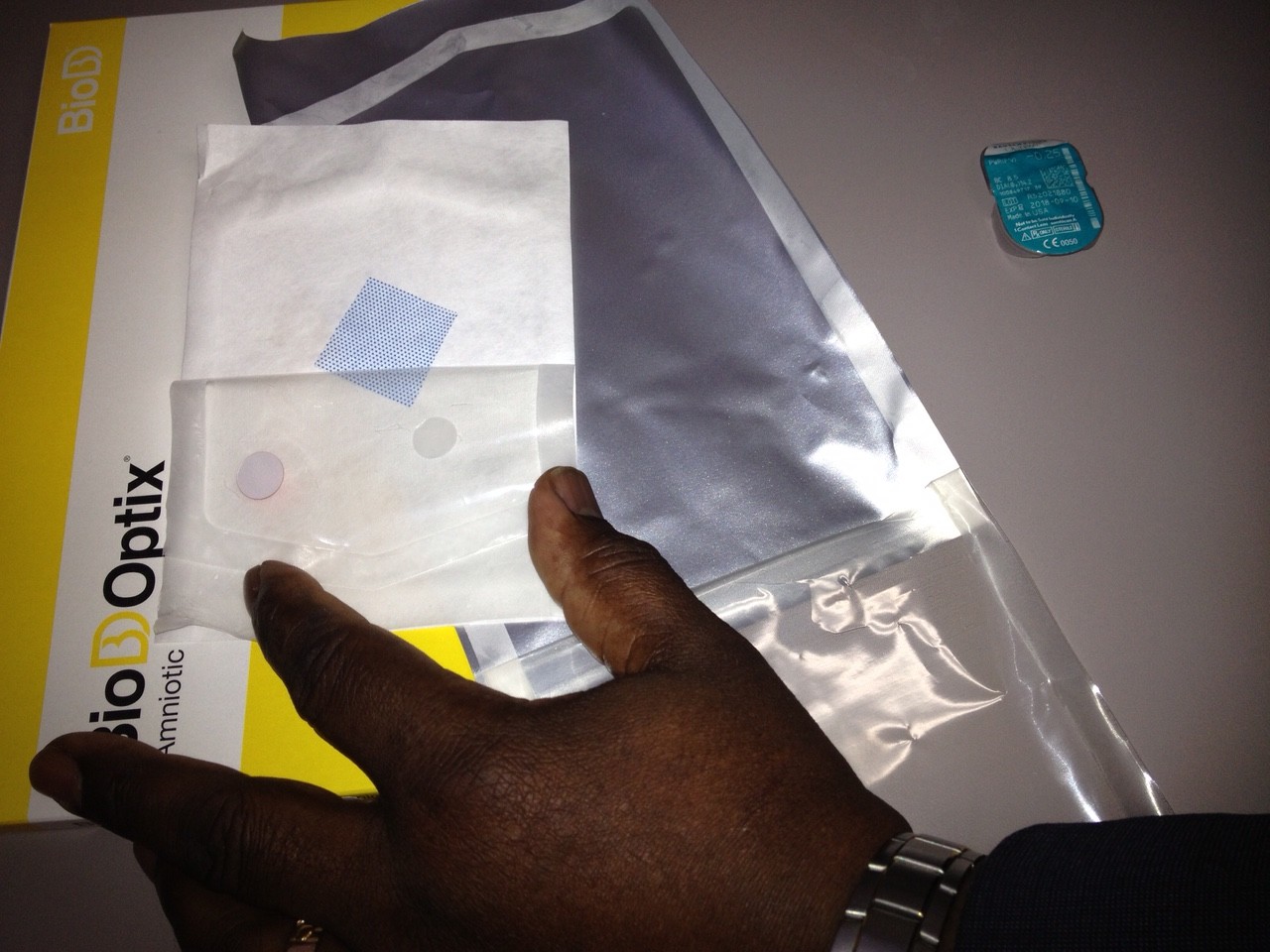
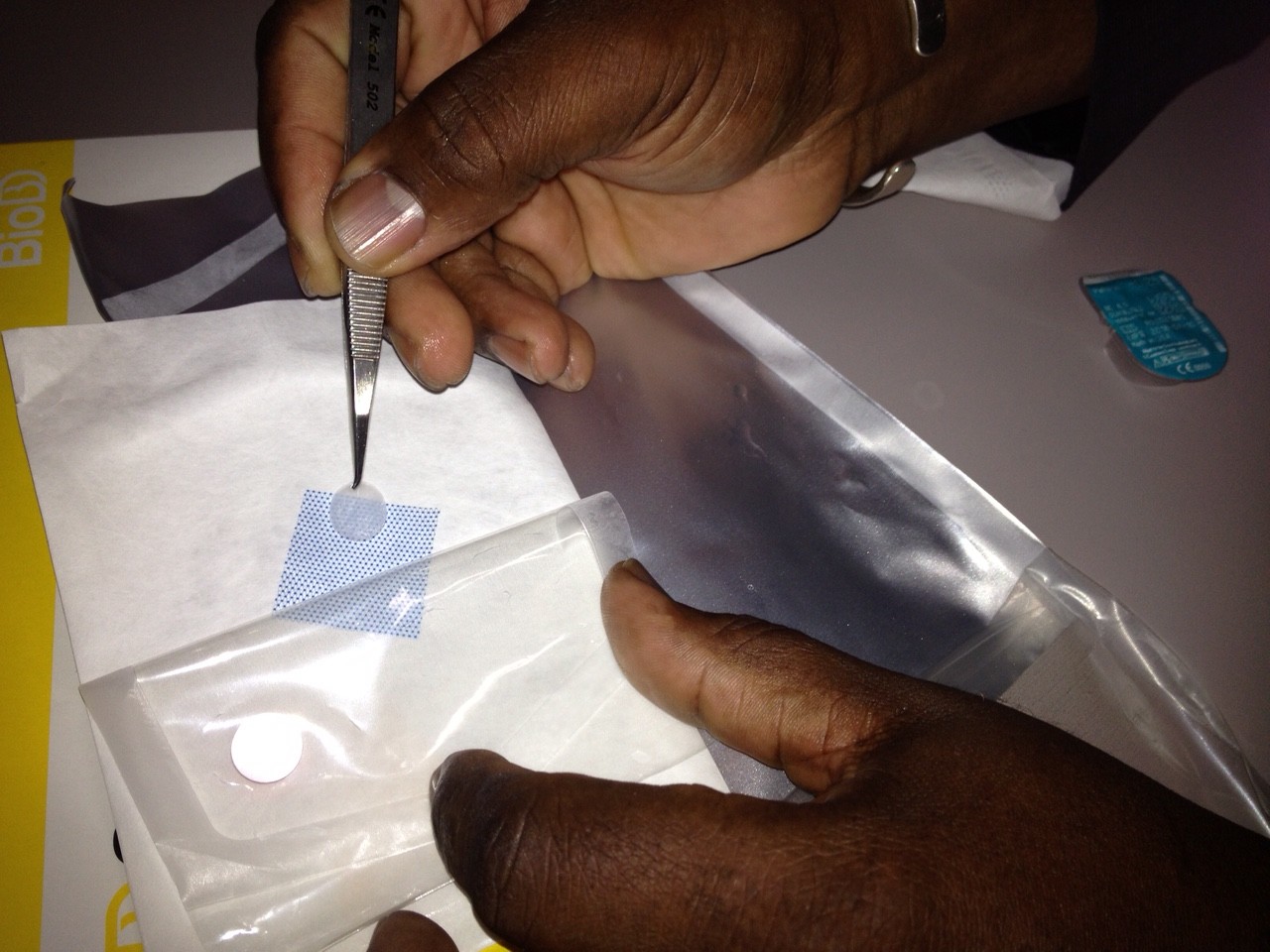
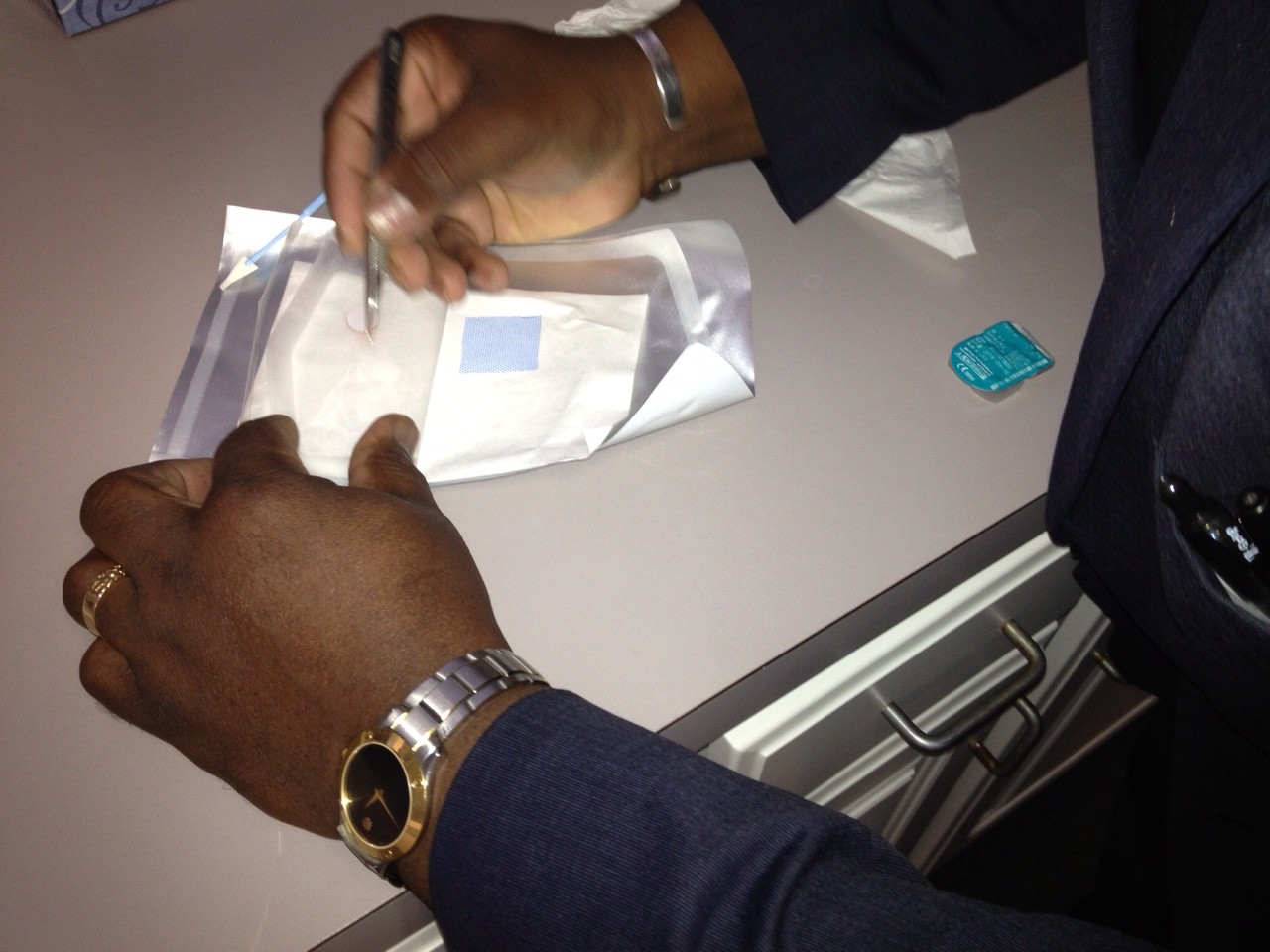
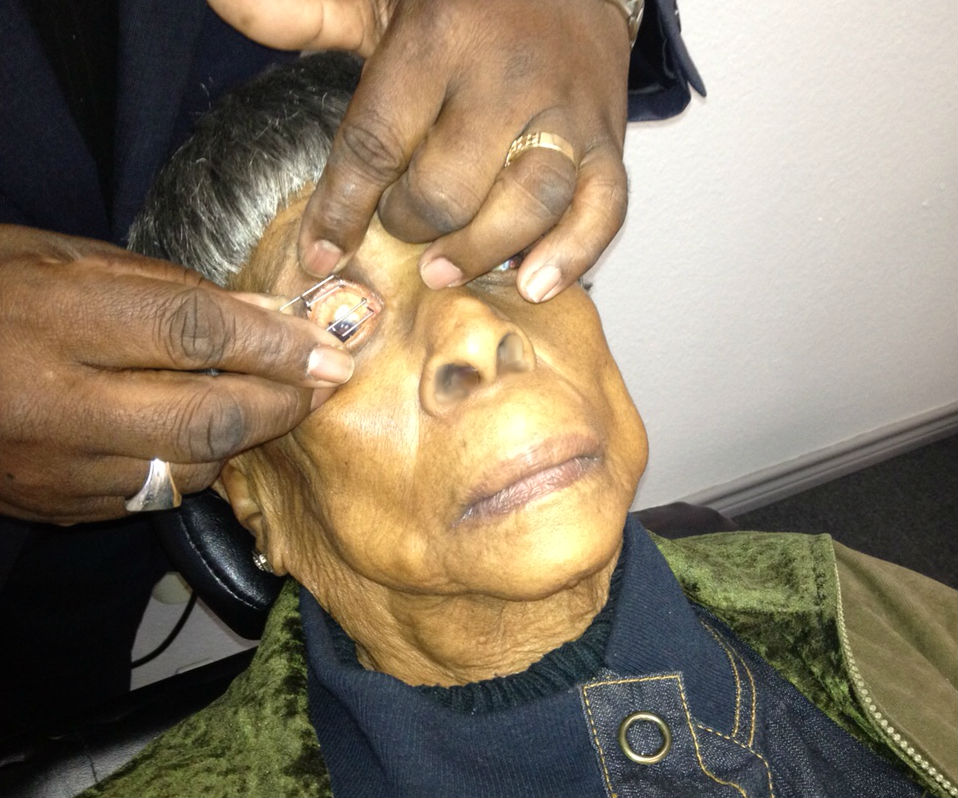
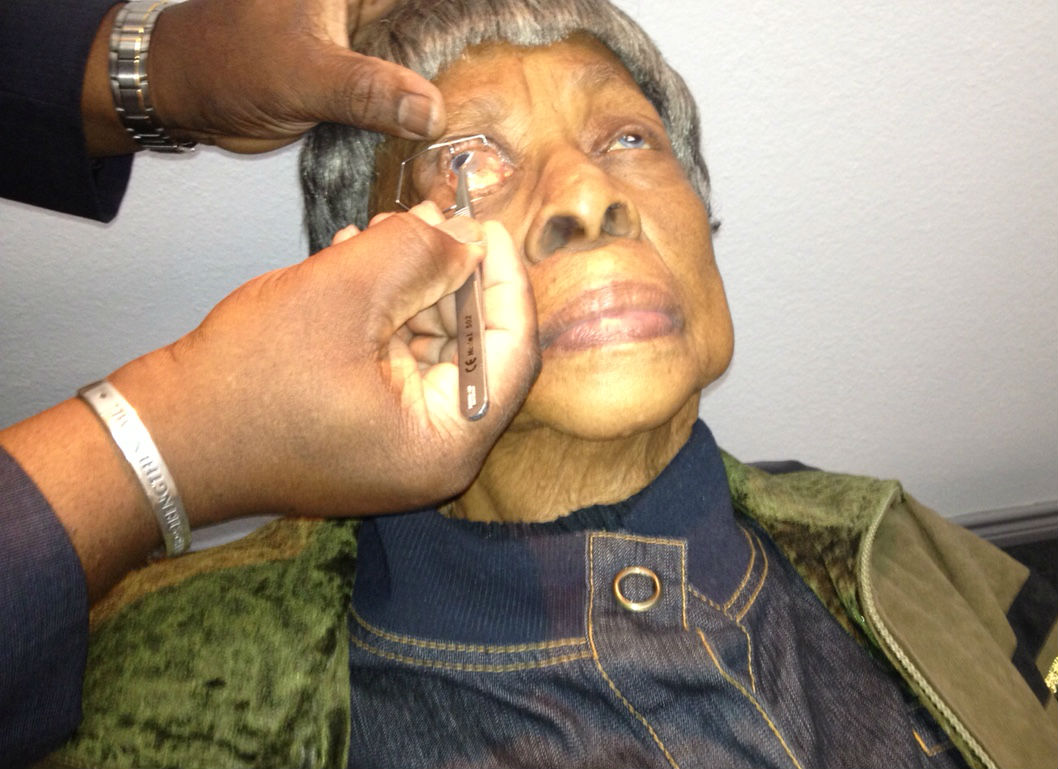
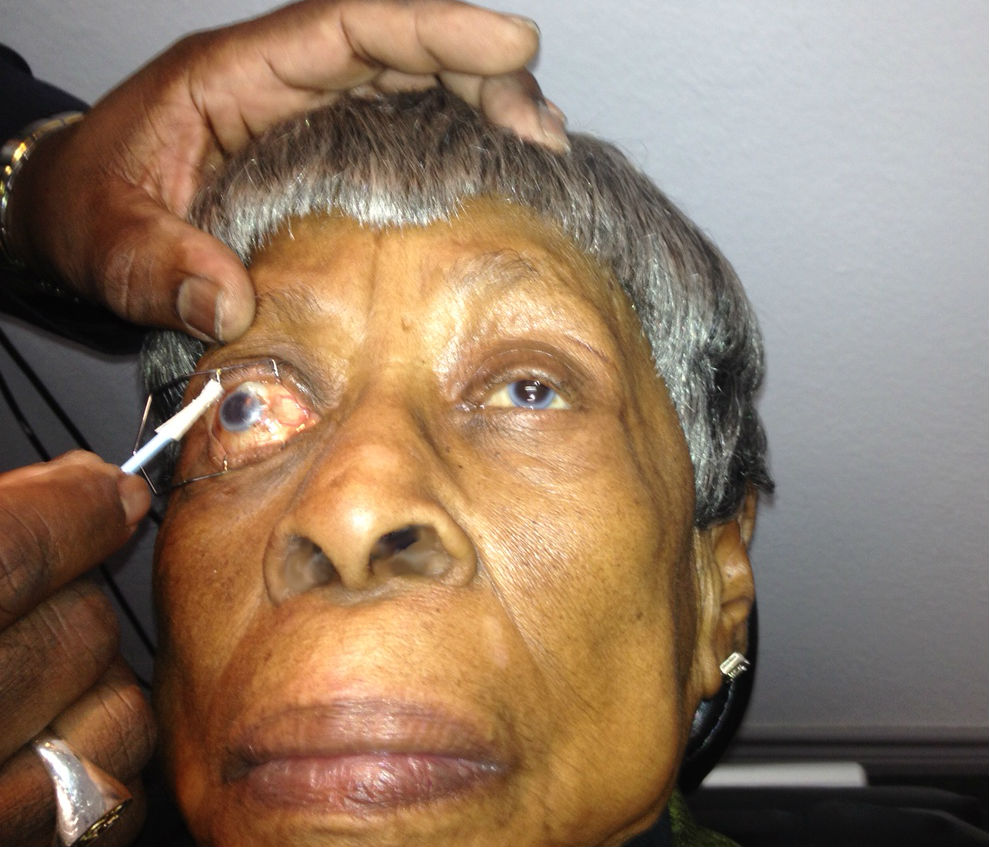
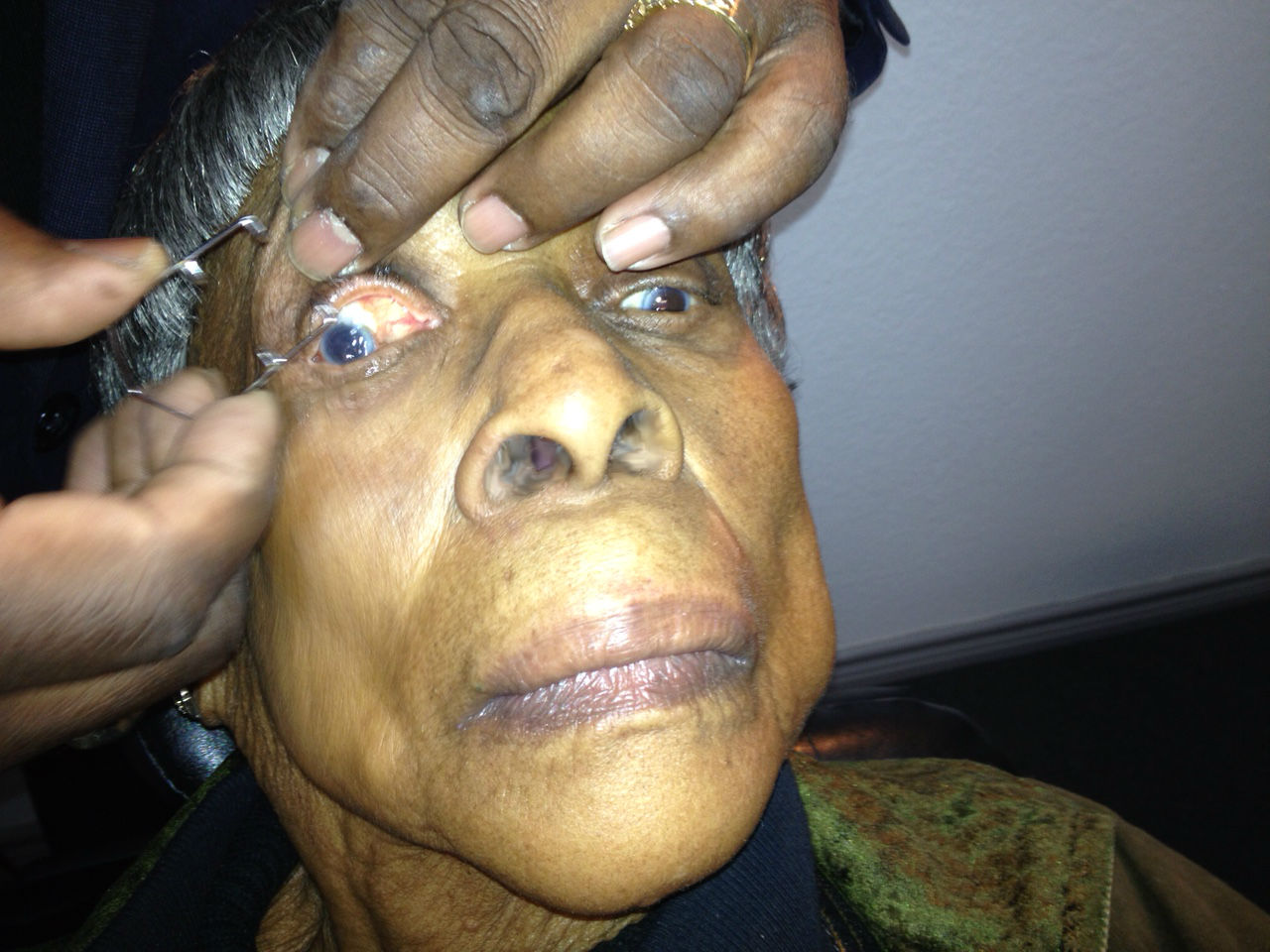
Amniotic Membrane Inserts
Protection of the irritated cornea can be accomplished with a standard bandage contact lens or application of a BioDOptix amnionic membrane insert.
An evaluation of the complete visual system was performed.
- Perform the eye examination that is medically necessary
- Provide the diagnostic tests or services that are medically necessary
- Properly document the services provided
- Code from the documentation
- Report the services to the payor
INITIAL EXAMINATION — DAY 1
| Diagnosis Code | Procedure Code | Modifier | Quantity | Payor | Amount Allowed |
| H16.223 - Keratoconjunctivitis sicca, not specified as Sjogren’s, bilateral | 65778 - Amniotic membrane placement | 1 | Medicare | 1464.30 | |
| H16.223 - Keratoconjunctivitis sicca, not specified as Sjogren’s, bilateral | 92285 - External ocular photography | 51 | 1 | Medicare | 15.36 |
| H52.213 - Irregular astigmatism, bilateral | 92025 - Corneal topography | 1 | Medicare | 39.45 | |
| Total | $1519.11 |
POSTOPERATIVE EXAMINATION — DAY 2
| Diagnosis Code | Procedure Code | Modifier | Quantity | Payor | Amount Allowed |
| H16.223 - Keratoconjunctivitis sicca, not specified as Sjogren’s, bilateral | 99212 - Level 2 Evaluation & Management | 1 | Medicare | 42.12 | |
| Total | $42.12 |
POSTOPERATIVE EXAMINATION — DAY 3
| Diagnosis Code | Procedure Code | Modifier | Quantity | Payor | Amount Allowed |
| H16.223 - Keratoconjunctivitis sicca, not specified as Sjogren’s, bilateral | 99212 - Level 2 Evaluation & Management | 1 | Medicare | 42.12 | |
| Total | $42.12 |
H16.221
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca,
not specified as Sjogren’s,
right eye
H16.222
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca,
not specified as Sjogren’s,
left eye
H16.223
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca,
not specified as Sjogren’s,
bilateral
370.33
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca, not specified as Sjogren’s
92285
External ocular photography
92132
Anterior segment imaging
92071
Bandage contact lens
68761
Punctal occlusion
92025
Corneal topography
65778
Amniotic membrane placement




 Print | Share
Print | Share