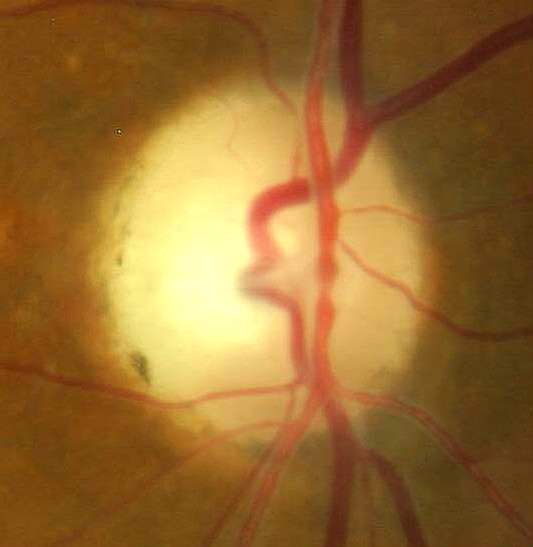
Optic disc edema that characterizes papilledema
ICD-10 Diagnosis Codes:
H47.11–Papilledema associated with increased intracranial pressure
H47.12–Papilledema associated with decreased ocular pressure
H47.13–Papilledema associated with retinal disorder
H47.141–Papilledema associated with Foster-Kennedy syndrome, right eye
H47.142–Papilledema associated with Foster-Kennedy syndrome, left eye
H47.143–Papilledema associated with Foster-Kennedy syndrome, bilateral
Title
Papilledema
Category
Disorders Of The Optic Nerve And The Visual Pathways
Description
Papilledema is optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure. The swelling is usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks
Papilledema is optic disc swelling that is secondary to elevated intracranial pressure. Vision is usually preserved with acute papilledema, despite other causes of optic disc swelling. Papilledema almost always presents as a bilateral phenomenon and may develop over hours to weeks.
The information currently being updated. Please check back later.
The main goal of the diagnostic evaluation in a patient with papilledema is to accomplish the following:
- Determine the etiology of the papilledema
- Identify and exclude any differential diagnosis
- Determine the monitoring schedule and prescribe a treatment program specific to the etiology
Patient History
Patients with papilledema may present with any of the following abnormal signs and sypmtoms:
- Sudden onset of unilateral vision loss
- Pain with eye movements
- Relative afferent pupillary defect
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
The following diagnostic tests are used to determine the extent of structural and functional damage from papilledema:
Refraction
- Measurement of visual function / visual acuity helps determine improvement of vision as the inflammation resolves
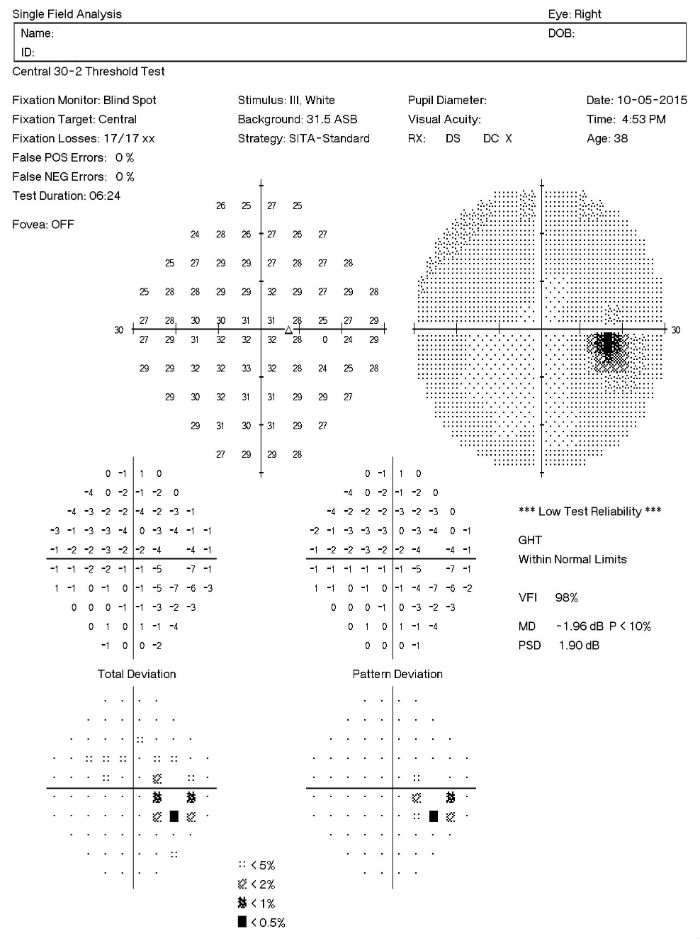
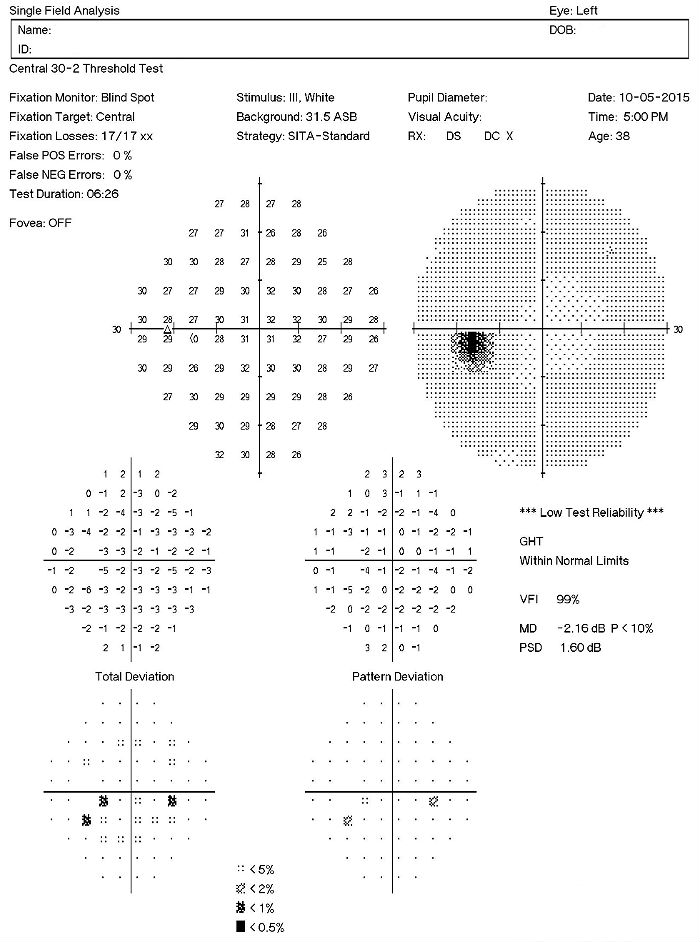
Visual Field Examination
- A visual field defect can be noted around the blind spot and the extent of edema corresponds to the visual field defect
- There may be an overall reduction in retinal sensitivity seen as well
 |
 |
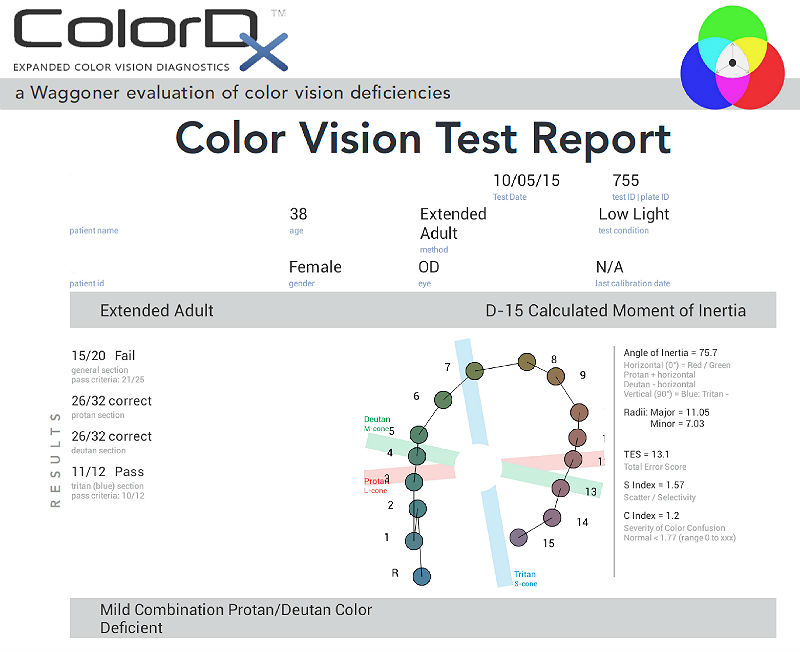
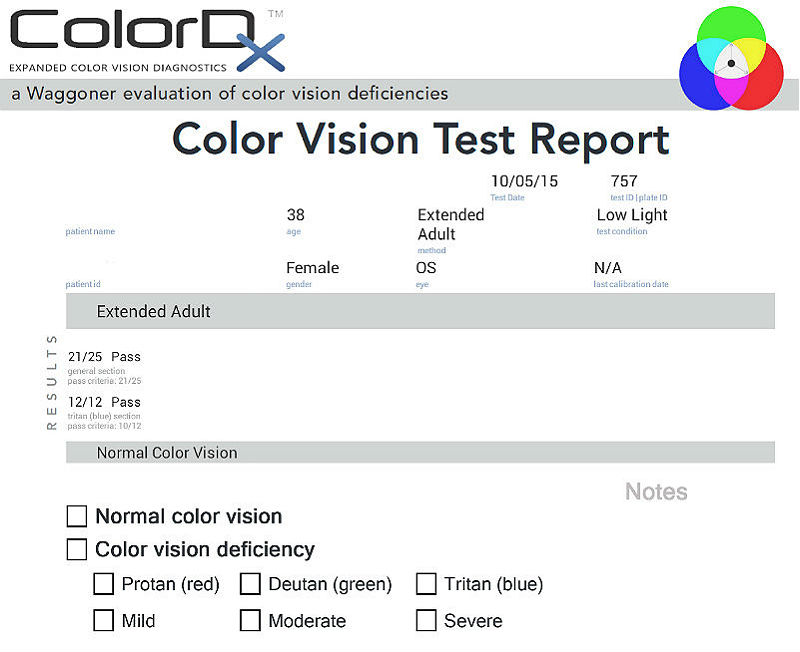
Color Vision Examination
- Patients can also have a decrease in color perception especially red hues appear dimmer
 |
 |
Extended Ophthalmoscopy
- Helps evaluate optic disc morphology and look for elevation of optic nerve
- Assist with documenting abnormal structural changes to the optic disc
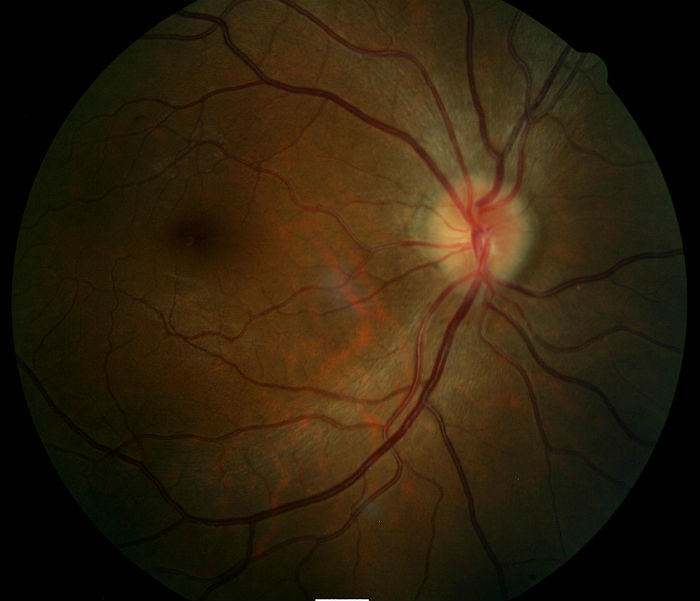
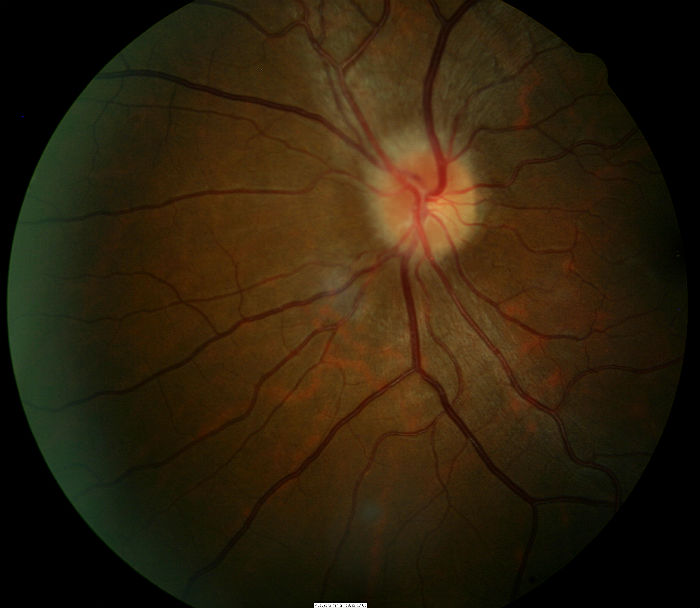
Fundus Photography
- Another means to evaluate optic disc morphology and elevation of optic nerve
- It can also assist in document abnormal structural changes to the optic disc
 |
 |
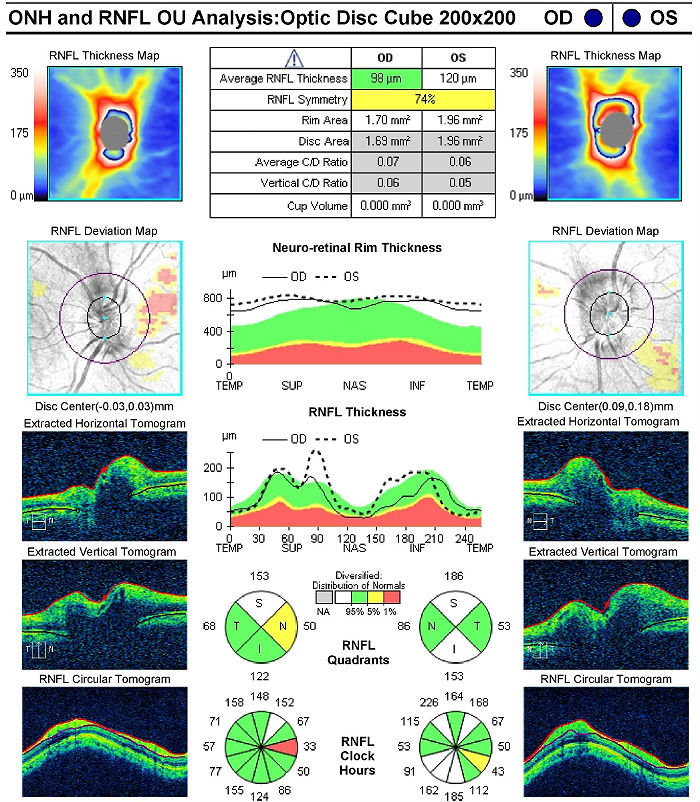
Retinal Scanning Laser
- Provides detail of the excavation of the optic disc
 |
Right Eye
Left Eye
Both Eyes
|
Pupillary Examination
An afferent pupillary defect may be noted if the condition is both significant and asymmetric.
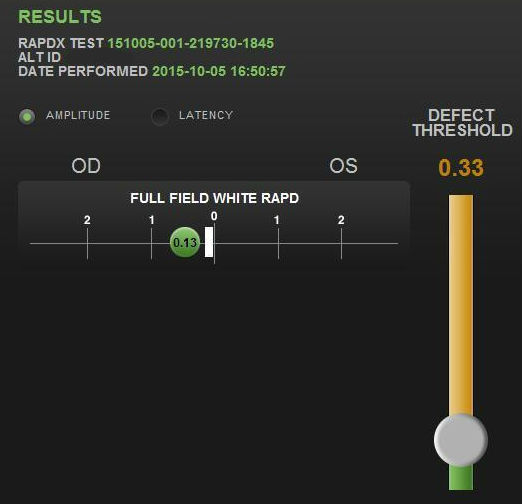
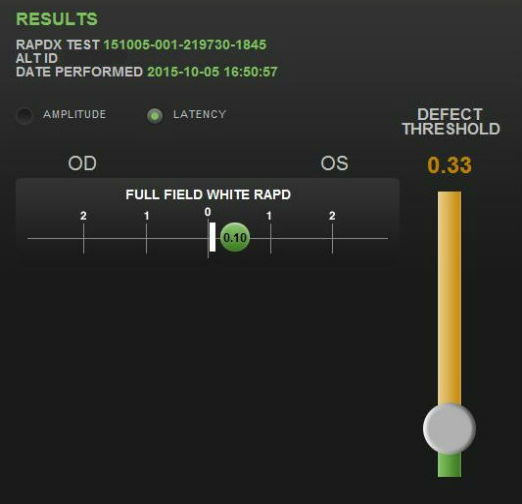
- RAPDx automated pupillary examination
- Assessment of pupillary response amplitude and velocity
- Index of defect numbers above 0.30 are considered abnormal
- Abnormal amplitude in the left eye indicates an afferent pupillary defect is present
 |
 |
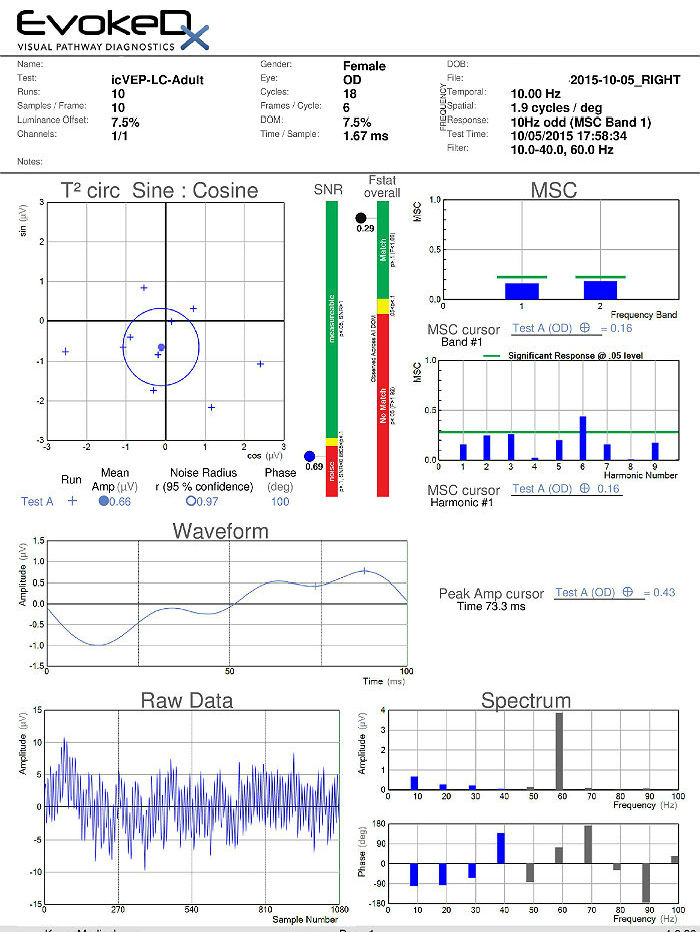
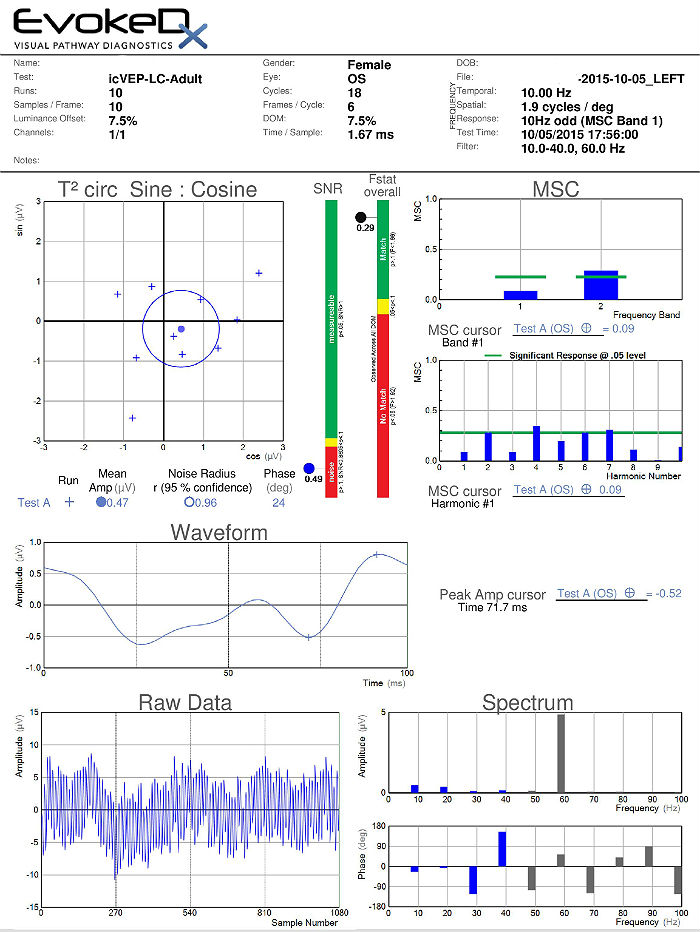
Visual Evoked Potential Testing
The visual evoked potential (VEP) is an objective electric sign of visual pathway function and its parameters are sensitive to abnormalities in the visual system. Measuring the conduction speed and magnitude of the neural response from the eye to the cortex can be helpful is assessing early changes in glaucoma. Although not diagnostic of glaucoma, abnormal VEP test results in addition to other abnormal clinical findings can assist in making the difficult diagnosis of early glaucomatous damage.
- VEP testing evaluates the integrity of the afferent visual sensory system
- The procedure can be accomplished with the EvokeDx Testing Device manufactured by Konan Medical
 |
 |
The information currently being updated. Please check back later.
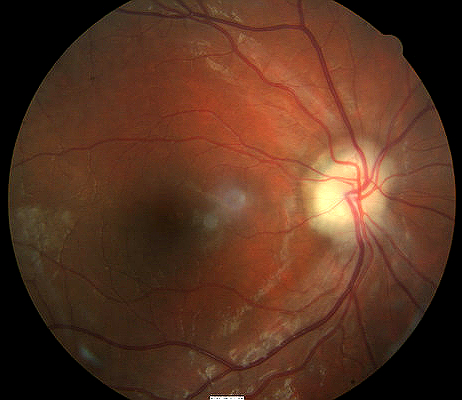 |
Optic Papillitis
|
Perineuritis
This type of optic neuritis is characterized by an inflammation of the optic nerve sheath. In this condition, the optic nerve is spared and vision loss is mild to moderate. Perineuritis usually affects older people and is commonly associate due to infectious or inflammatory conditions (e.g., sarcoidosis). Perineuritis is not associated with multiple sclerosis.
Neuroretinitis
This type of optic neuritis may occur at any age. It is characterized by concomitant swelling of optic disc and macula. In severe presentation, exudates form around the macula to give the appearance of a macular star. Neuroretinitis is not associated with multiple sclerosis.
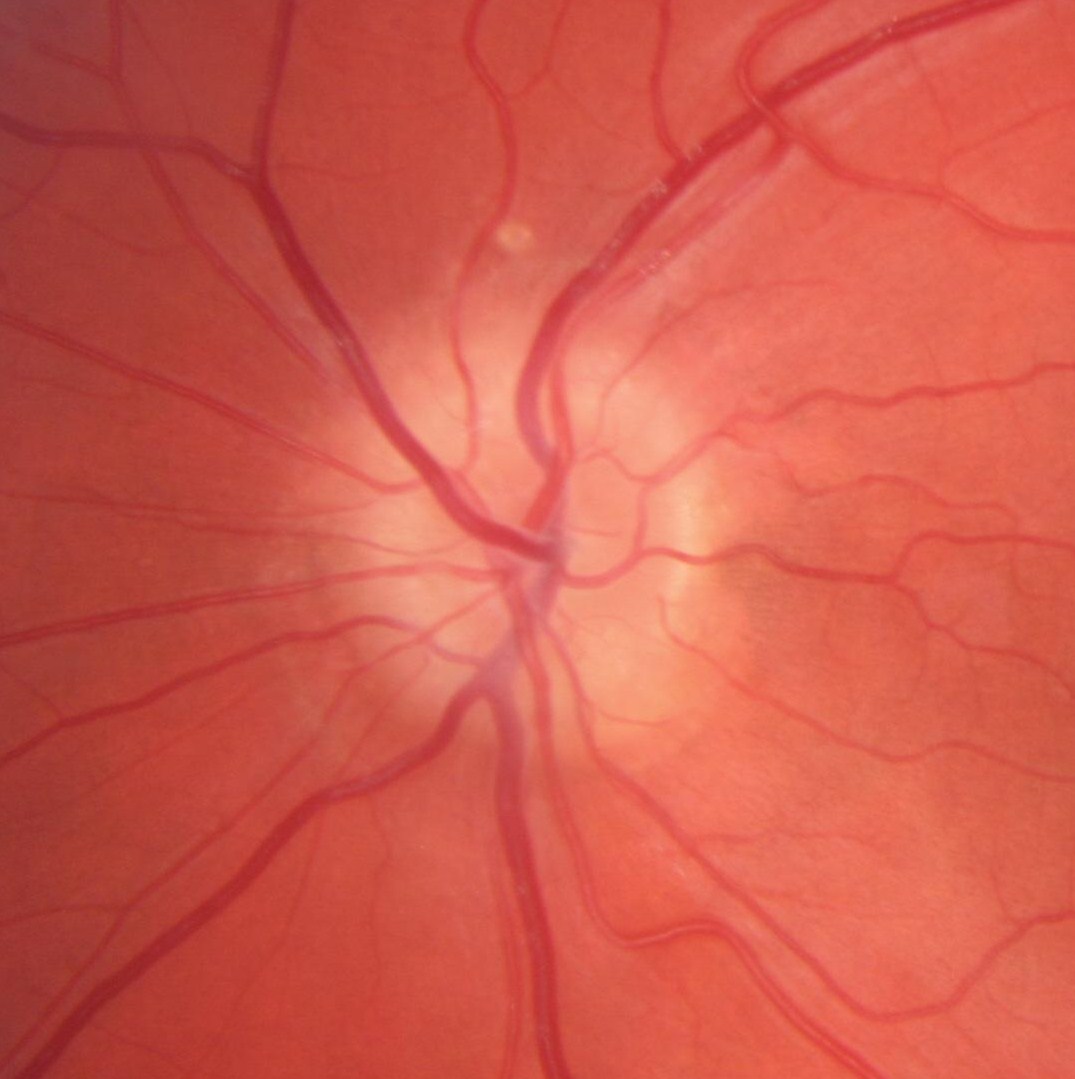 |
Optic Nerve Drusen
|
The information currently being updated. Please check back later.
1. Gossman M. Papilledema. Medscape/EMedicine. 6 Oct 2015. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1217204-overview#showall. Last accessed October 15, 2015.
377.01
Papilledema associated with increased intracranial pressure
92015
Refraction
92083
Visual field examination
92250
Fundus photography
92225
Extended ophthalmoscopy
92226
Subsequent ophthalmoscopy
95930
Visual evoked potential
92275
Electroretinography
92283
Color vision examination
92134
Macular OCT scan
92133
Retinal laser scan
Occurrence
Distribution
Risk Factors




 Print | Share
Print | Share